One of the best sources for scanner information available is the RadioReference.com database. This is a huge listing of frequencies used thruout the USA and Canada for all types of two-way radio operations.
If you do your own scanner programming then the RRDB is invaluable for information. It is usually more accurate than the agencies themselves have! Even if you only use a database scanner (like a HomePatrol or TRX) then it helps to understand the database so you will have a better idea of what you are listening to. Remember: The data in your scanner came from RadioReference in the first place.
To read the RadioReference database and understand how it works you need to understand how it works. Without understanding how it is laid out it can be daunting, there is a whole lot of information at your fingertips.
To understand it you need to know a couple things. There are two main types of data available, trunked and conventional.
First we will look at a conventional frequency listing. Then we will look at trunking information. (Conventional means that it is not trunked.)
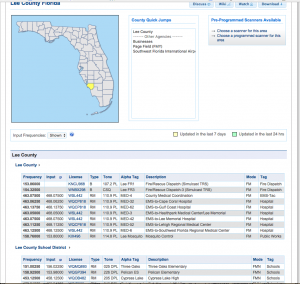
Here is the frequency page for Lee County Florida. It shows several fields:
- Frequency (Actual frequency used or the repeater output)
- Input (Repeater inputs)
- License FCC Callsign, click on this to see what frequencies and other info is available for it.
- Type Base, Repeater, Mobile only etc.
- Tone Could be PL, DPL or NAC 9for P25) etc.
- Alpha Tag A short tag used on some scanners, akin to channel numbers etc.
- Description A longer description of the channel and its use.
- Mode FM, AM, Digital etc.
- Tag The classification that the channel falls under.
If you hover over the column title it will tell you what the codes mean.
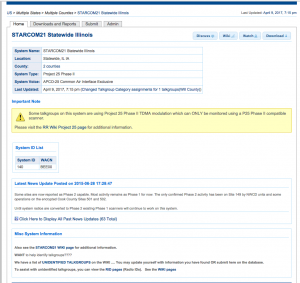
Since so many areas use trunking systems these days one might miss a lot of the info needed to monitor the area. Look at the bottom of the county’s page to see a list of trunking systems active in the county. If you see one that appears to be used there click on it to see the data. The first part you will see it the basic info:
At the top you will see an info box with the system name, location, type and other info. Below that you will see the System ID’s (some scanners will show the System ID to identify it) and other info.
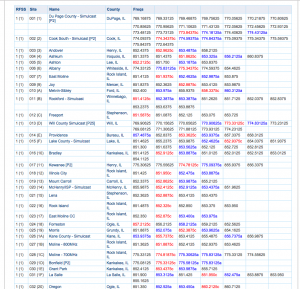
If you scroll down the page next you will see the trunked system Sites. Sites is where you will find the actual frequencies used by the system. Some systems only have 1 or 2 Sites, others (like the one shown) have dozens.
This is a portion of the Site List for the huge Illinois StarCom21 system that has many sites all over the state. There are several columns:
- RFSS is the Zone number (RF Subsystem), then the Site Number within the Zone. Sometimes Sties are shown in other contexts as X-YYY (1-012 meaning Zone 1, Site 12) or just XYY (112).
- Next is the Site Name, usually the city or location the site is located in. The county the site is in follows.
- Last are the frequencies used at that Site. Some freqs will be shown in red, these are known to be “Primary” control channels (mostly for P25 systems). Other freqs will be in blue, these are known to be “Alternate” control channels. The rest are shown in black, these are not know to be used as control channels but are used for voice. Unless you know for sure otherwise, it is usually best to include all channels of the Site in your scanner.
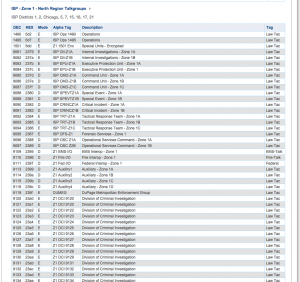
The last part of the Trunked system information is the Talkgroup List. These are the virtual channels used to allow the correct people to communicate within the system.
The columns here are:
- DEC (Decimal) The most common way to identify a talkgroup in scanners.
- HEX (Hexidecimal) Another way to view Talkgroups, used mostly by the fleet radios.
- Mode Tells you if it is Digital (D), Analog (A), Encrypted (E) or TDMA (T).
- Alpha Tag The short channel name
- Description More inclusive description of the channel and its use
- Tag The classification (Service Type) for that talkgroup.
By understanding the way the data is laid out you can apply this to your programming and understanding of the systems you listen to.